SAP S/4HANA Implementation: 7 Proven Steps for Ultimate Success
Implementing SAP S/4HANA can transform your business—but only if done right. Discover the ultimate roadmap to a seamless, powerful, and future-ready SAP S/4HANA implementation that drives real ROI.
Understanding SAP S/4HANA Implementation: The Big Picture

SAP S/4HANA is not just another ERP upgrade—it’s a digital transformation engine. At its core, SAP S/4HANA Implementation redefines how enterprises manage data, processes, and decision-making by leveraging in-memory computing through SAP HANA. Unlike legacy SAP ERP systems, S/4HANA offers real-time analytics, simplified data models, and embedded AI capabilities.
What Sets SAP S/4HANA Apart?
The shift from traditional ERP to SAP S/4HANA is revolutionary. With its columnar data storage and in-memory processing, S/4HANA enables lightning-fast data retrieval and processing. This means financial closing that takes minutes instead of days, live inventory tracking, and predictive analytics embedded directly into transactional systems.
- Real-time processing powered by SAP HANA database
- Simplified data model with elimination of aggregates and indices
- Intelligent enterprise capabilities with embedded AI and machine learning
- Modern user experience via SAP Fiori
“SAP S/4HANA is not an IT project—it’s a business transformation initiative.” — SAP Executive Board
Why Companies Are Migrating Now
With SAP ending mainstream maintenance for ECC by 2027, organizations are under pressure to migrate. But beyond compliance, businesses are embracing SAP S/4HANA Implementation to gain agility, reduce TCO (Total Cost of Ownership), and unlock innovation. Industries from manufacturing to retail are leveraging S/4HANA to automate supply chains, optimize logistics, and enable end-to-end digital processes.
According to SAP’s official roadmap, over 14,500 customers have already adopted S/4HANA globally, with more than 60% running mission-critical operations on the platform.
Key Benefits of SAP S/4HANA Implementation
A successful SAP S/4HANA Implementation delivers measurable business value across departments. From finance to logistics, the platform enhances speed, accuracy, and strategic insight. Let’s explore the tangible benefits driving adoption.
Real-Time Analytics and Decision-Making
One of the most transformative aspects of SAP S/4HANA Implementation is the ability to access live data across the enterprise. Traditional ERP systems rely on batch processing and data replication, leading to delays. S/4HANA eliminates this lag.
- Instant financial reporting with universal journal (ACDOCA table)
- Live dashboards for supply chain visibility
- Predictive analytics for demand forecasting and risk management
For example, a global manufacturer reduced month-end closing from 10 days to under 24 hours post-implementation.
Operational Efficiency and Process Simplification
SAP S/4HANA Implementation streamlines business processes by removing redundant transactions and simplifying data structures. The system consolidates multiple legacy tables into single, unified views.
- Material Ledger becomes mandatory, enabling real-time costing
- Logistics processes like MRP and inventory management are optimized
- Finance modules integrate seamlessly with procurement and sales
This simplification reduces system complexity, lowers maintenance costs, and improves data integrity.
Enhanced User Experience with SAP Fiori
Modern users expect intuitive, mobile-friendly interfaces. SAP S/4HANA Implementation includes SAP Fiori, a role-based, responsive UI that works across devices.
- Over 700 standard Fiori apps available
- Customizable dashboards for executives and operational staff
- Touch-enabled workflows for warehouse and field workers
Companies report up to 30% increase in user productivity after deploying Fiori apps.
Choosing the Right SAP S/4HANA Implementation Approach
There is no one-size-fits-all path to SAP S/4HANA. Organizations must evaluate their current landscape, business goals, and technical readiness to select the optimal approach. The three primary methods are system conversion, new implementation, and landscape transformation.
System Conversion (Brownfield Approach)
The brownfield approach involves converting an existing SAP ERP system directly to SAP S/4HANA. This method preserves historical data, custom code, and business processes while upgrading the underlying technology stack.
- Fastest route for SAP ERP customers
- Minimizes business disruption
- Requires extensive code remediation (via SAP Readiness Check)
However, it may carry forward legacy inefficiencies. Companies using this path must invest in cleanup and optimization.
Learn more about the conversion process at SAP Help Portal.
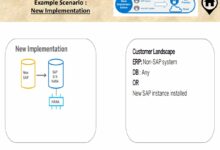
New Implementation (Greenfield Approach)
The greenfield approach means starting fresh with SAP S/4HANA. It’s ideal for organizations looking to redesign processes and eliminate technical debt.
- Opportunity to adopt best practices
- Minimal legacy baggage
- Longer timeline and higher initial effort
This method is often chosen by companies undergoing mergers, entering new markets, or launching digital transformation initiatives. While costly upfront, it delivers a cleaner, more agile system long-term.
Landscape Transformation (Bluefield Approach)
Introduced by SAP, the bluefield approach blends elements of brownfield and greenfield. It allows selective migration of business units or processes while keeping others on legacy systems.
- Enables phased transformation
- Supports hybrid landscapes
- Ideal for large, complex organizations
For instance, a multinational corporation might migrate its European division via greenfield while converting its Asian operations via brownfield, all under a unified S/4HANA strategy.
The SAP Activate Methodology: Your Implementation Roadmap
SAP Activate is the official framework for SAP S/4HANA Implementation. It combines agile principles, preconfigured content, and guided configuration to accelerate deployment and reduce risk.
Phases of SAP Activate
SAP Activate is structured into five distinct phases, each with clear deliverables and milestones.
- Prepare: Project setup, team onboarding, and system provisioning
- Explore: Fit-to-standard workshops to align business processes with SAP best practices
- Realize: Configuration, integration, data migration, and testing
- Deploy: Final validation, cutover planning, and go-live
- Run: Post-go-live support, continuous improvement, and optimization
Each phase uses pre-built SAP Best Practices, reducing customization needs and speeding up time-to-value.
Fit-to-Standard vs. Customize-to-Fit
A critical decision in SAP S/4HANA Implementation is whether to adapt business processes to standard SAP functionality (fit-to-standard) or modify the system to fit existing processes (customize-to-fit).
- Fit-to-standard reduces complexity, lowers TCO, and ensures easier upgrades
- Customize-to-fit offers flexibility but increases risk and maintenance burden
SAP recommends a 80:20 rule—adopt standard processes wherever possible, and customize only for true differentiators.
“The goal is not to replicate your old system, but to reinvent your business.” — SAP Activate Guide
Role of SAP Best Practices and Rapid Deployment
SAP provides over 150 industry-specific Best Practices for SAP S/4HANA Implementation. These are pre-configured scenarios delivered as Solution Packages in SAP Cloud ALM or on-premise systems.
- Accelerate implementation by up to 50%
- Include test scripts, documentation, and training materials
- Support rapid deployment for mid-sized businesses
For example, the “Integrated Financials for SAP S/4HANA” package covers core accounting, asset management, and intercompany processes out-of-the-box.
Data Migration and System Integration in SAP S/4HANA Implementation
Data is the lifeblood of any ERP system. A successful SAP S/4HANA Implementation hinges on accurate, clean, and timely data migration from legacy systems.
Strategies for Effective Data Migration
Data migration is not just a technical task—it’s a business-critical process that requires planning, cleansing, and validation.
- Use SAP Migration Cockpit for structured data transfer
- Leverage pre-mapping templates for common objects (customers, vendors, GL accounts)
- Perform multiple test migrations to validate accuracy
Key challenges include handling large data volumes, ensuring referential integrity, and managing master data harmonization across subsidiaries.
Master Data Governance and Harmonization
Poor master data quality is a leading cause of implementation failure. SAP S/4HANA Implementation must include a robust Master Data Governance (MDG) strategy.
- Define global data standards for materials, customers, and vendors
- Implement data stewardship roles and workflows
- Use SAP MDG or third-party tools for centralized control
One automotive supplier reduced duplicate vendor records by 70% before migration, significantly improving procurement efficiency.
Integration with External Systems
SAP S/4HANA rarely operates in isolation. It must integrate with CRM, HR, MES, and third-party logistics systems.
- Use SAP PI/PO or SAP Cloud Integration for middleware
- Leverage OData APIs and IDocs for real-time connectivity
- Adopt SAP API Business Hub for discovering and consuming APIs
For cloud-centric architectures, SAP Integration Suite provides a unified platform for hybrid integration scenarios.
Change Management and Organizational Readiness
Technology alone doesn’t guarantee success. SAP S/4HANA Implementation is as much about people as it is about systems. Without proper change management, even the most technically sound project can fail.
Building a Change Management Strategy
A structured change management plan addresses resistance, builds buy-in, and ensures user adoption.
- Engage stakeholders early—from executives to shop floor workers
- Communicate benefits clearly and consistently
- Establish a network of change champions across departments
Prosci’s ADKAR model (Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability, Reinforcement) is widely used in SAP projects to guide behavioral change.
Training and User Adoption
With SAP Fiori’s modern interface, training needs are different from legacy SAP GUI. Organizations must adopt blended learning approaches.
- Role-based training paths (e.g., finance user vs. warehouse clerk)
- Interactive e-learning modules and sandbox environments
- Just-in-time learning via embedded help and videos
One pharmaceutical company achieved 95% user adoption within 3 months by launching a gamified training portal.
Post-Go-Live Support and Hypercare
The first 30–90 days after go-live are critical. Hypercare is an intensive support phase where implementation partners and internal teams work side-by-side to resolve issues.
- Establish a dedicated support desk with SLAs
- Monitor system performance and user feedback
- Conduct daily war room meetings to triage incidents
Hypercare ensures stability and builds confidence in the new system.
Common Challenges in SAP S/4HANA Implementation and How to Overcome Them
Despite its benefits, SAP S/4HANA Implementation is complex. Organizations face technical, organizational, and strategic hurdles. Recognizing these early is key to mitigation.
Custom Code Remediation
Legacy SAP ERP systems often contain thousands of lines of custom ABAP code. Not all of it is compatible with S/4HANA.
- Run SAP Readiness Check to identify incompatible code
- Use ABAP Test Cockpit and ATC for static code analysis
- Refactor or replace obsolete enhancements with SAP BAdIs or side-by-side extensions
One financial services firm reduced its custom codebase by 60% during remediation, improving system performance and upgradeability.
Data Volume and Performance Issues
While SAP HANA handles large datasets efficiently, poor data management can still impact performance.
- Implement data aging and archiving strategies using ILM (Information Lifecycle Management)
- Optimize database indexes and partitioning
- Monitor system health with SAP EarlyWatch Alert
Regular housekeeping ensures sustained performance post-implementation.
Scope Creep and Project Delays
Uncontrolled requirements and shifting priorities are common in SAP S/4HANA Implementation.
- Define a clear project scope during the Explore phase
- Use agile sprints to deliver incremental value
- Establish a formal change request process
Stakeholder alignment and strong project governance are essential to keep timelines on track.
Future-Proofing Your SAP S/4HANA Investment
Going live is not the end—it’s the beginning. To maximize ROI, organizations must evolve their SAP S/4HANA environment continuously.
Leveraging AI and Machine Learning
SAP S/4HANA embeds intelligent technologies to automate routine tasks and provide insights.
- Cash Application uses ML to auto-match payments
- Intelligent Robotic Process Automation (RPA) for invoice processing
- Predictive maintenance for asset-intensive industries
These capabilities reduce manual effort and improve accuracy over time.
Cloud Evolution and Subscription Models
SAP is pushing toward cloud-first. SAP S/4HANA Cloud offers faster innovation cycles, automatic updates, and lower infrastructure overhead.
- Public cloud: Fully managed by SAP, ideal for standard processes
- Private cloud: Hosted in hyperscalers (AWS, Azure, GCP) with more control
- Hybrid: Mix of cloud and on-premise for complex landscapes
Many companies start on-premise and plan a cloud transition within 3–5 years.
Continuous Innovation with SAP BTP
The SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) enables extension and innovation beyond core S/4HANA.
- Build custom apps with SAP Build
- Integrate with LoB systems using SAP Integration Suite
- Enable advanced analytics with SAP Analytics Cloud
BTP turns SAP S/4HANA into a digital innovation hub.
What is SAP S/4HANA Implementation?
SAP S/4HANA Implementation is the process of deploying SAP’s next-generation ERP suite, either by upgrading from legacy SAP systems or implementing it anew. It involves technical migration, business process redesign, data conversion, and organizational change to leverage real-time computing and intelligent enterprise capabilities.
What are the main implementation approaches?
The three main approaches are: 1) Brownfield (system conversion), 2) Greenfield (new implementation), and 3) Bluefield (selective landscape transformation). Each has trade-offs in speed, cost, and business disruption.
How long does SAP S/4HANA Implementation take?
Timelines vary: Greenfield implementations take 12–18 months, brownfield 6–12 months, and rapid deployments can go live in under 6 months using SAP Best Practices.
Is SAP S/4HANA only for large enterprises?
No. While initially targeted at large firms, SAP now offers scalable editions for mid-sized businesses, including cloud-based and industry-specific solutions.
What happens after SAP ECC maintenance ends?
Mainstream maintenance for SAP ECC ends in 2027. After that, SAP will no longer provide updates or security patches, making migration to S/4HANA essential for continued support and innovation.
Implementing SAP S/4HANA is a strategic imperative, not just a technical upgrade. From choosing the right approach to managing change and leveraging AI, success requires a holistic strategy. By following proven methodologies like SAP Activate, prioritizing data quality, and investing in people, organizations can unlock the full potential of the intelligent enterprise. The journey is complex, but with the right roadmap, the rewards—agility, insight, and innovation—are transformative.
Further Reading: